本系列连载文章:
- 七天搞定SAS(七):常用统计模型
- 七天搞定SAS(六):宏的编写、程序调错
- 七天搞定SAS(五):数据操作与合并
- 七天搞定SAS(四):数据输出
- 七天搞定SAS(三):基本模块调用(格式、计数、概要统计、排序等)
- 七天搞定SAS(二):基本操作(判断、运算、基本函数)
- 七天搞定SAS(一):数据的导入、数据结构
搞定基本的函数之后,开始鼓捣SAS里面的模型。也就是说,要开始写PROC了。说实话,越学SAS,越觉得SAS像Stata...无论是从输出的样式,还是语法。好不习惯没有()的模型调用呀。若是说SAS和Stata的区别,怕只是Stata更侧重于计量模型而SAS则是服务于大多数统计模型吧。
PROC的基本内容:CONTENT
先是一个最基本的PROC:content,可以显示数据集的主要特性。比如,
LIBNAME tropical 'c:\MySASLib'; PROC CONTENTS DATA = tropical.banana;
这里主要是两个声明:TITLE和FOOTNOTE。前者输出时候会产生一个标题,后者会产生尾注。用法也是比较直接的:
TITLE ”Here’s another title”; TITLE ’Here’’s another title’; FOOTNOTE3 ’This is the third footnote’;
最后还有一个很像Stata的LABEL声明:
LABEL ReceiveDate = ’Date order was received’ ShipDate = ’Date merchandise was shipped’;
可以变量加注释。其实R里面给变量加注释是一件非常麻烦的事情,只有少数几个包可以搞定,还非常不值的。一般说来,我尽量在变量命名的时候长一点,这样直接可以读懂;再就是重建一个新的表,存储变量名和label。
SAS PROC求子集:WHERE
如果要在PROC里面先求子集的话,可以直接调用WHERE。感觉这里和SQL的思路比较像。用法也算是比较简单(SAS里面的用法都不是很麻烦,除了某些模型):
PROC PRINT DATA = 'c:\MySASLib\style'; WHERE Genre = 'Impressionism'; TITLE 'Major Impressionist Painters'; FOOTNOTE 'F = France N = Netherlands U = US'; RUN;
这样最终得到的结果就是:
Major Impressionist Painters 1 Obs Name Genre Origin 1 Mary Cassatt Impressionism U 3 Edgar Degas Impressionism F 5 Claude Monet Impressionism F 6 Pierre Auguste Renoir Impressionism F F = France N = Netherlands U = US
SAS PROC 数据进行排序:SORT
排序就更简单了,直接PROC SORT就可以了。
DATA marine; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Lengths.dat'; INPUT Name $ Family $ Length @@; RUN; * Sort the data; PROC SORT DATA = marine OUT = seasort NODUPKEY; BY Family DESCENDING Length; PROC PRINT DATA = seasort; TITLE 'Whales and Sharks'; RUN;
这样数据就按照Family、Length(递减)排序了。
Whales and Sharks 1 Obs Name Family Length 1 humpback 50.0 2 whale shark 40.0 3 basking shark 30.0 4 mako shark 12.0 5 dwarf shark 0.5 6 blue whale 100.0 7 sperm whale 60.0 8 gray whale 50.0 9 killer whale 30.0 10 beluga whale 15.0
SAS PROC 输出数据:PRINT
最简单的数据输出怕就是PRINT了,顾名思义,直接打印数据出来。这里可以进行便啦的选择,还就可以选择统计量:
DATA sales; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Candy.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-11 Class @15 DateReturned MMDDYY10. CandyType $ Quantity; Profit = Quantity * 1.25; PROC SORT DATA = sales; BY Class; PROC PRINT DATA = sales; BY Class; SUM Profit; VAR Name DateReturned CandyType Profit; TITLE 'Candy Sales for Field Trip by Class'; RUN;
得到的结果为:
Candy Sales for Field Trip by Class 1 -------------------------------- Class=14 --------------------------------- Date Candy Obs Name Returned Type Profit 1 Nathan 17612 CD 23.75 2 Matthew 17612 CD 17.50 3 Claire 17613 CD 13.75 4 Chris 17616 CD 7.50 5 Stephen 17616 CD 12.50 ----- ------ Class 75.00 -------------------------------- Class=21 --------------------------------- Date Candy Obs Name Returned Type Profit 6 Adriana 17612 MP 8.75 7 Caitlin 17615 CD 11.25 8 Ian 17615 MP 22.50 9 Anthony 17616 MP 16.25 10 Erika 17616 MP 21.25 ----- ------ Class 80.00 ====== 155.00
SAS PROC里面改变输出格式:FORMAT
基本就是FORMAT一下就可以了,再就是PUT的时候也可以调整。
DATA sales; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Candy.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-11 Class @15 DateReturned MMDDYY10. CandyType $ Quantity; Profit = Quantity * 1.25; PROC PRINT DATA = sales; VAR Name DateReturned CandyType Profit; FORMAT DateReturned DATE9. Profit DOLLAR6.2; TITLE 'Candy Sale Data Using Formats'; RUN;
输出结果为:
Candy Sale Data Using Formats 1 Date Candy Obs Name Returned Type Profit 1 Adriana 21MAR2008 MP $8.75 2 Nathan 21MAR2008 CD $23.75 3 Matthew 21MAR2008 CD $17.50 4 Claire 22MAR2008 CD $13.75 5 Caitlin 24MAR2008 CD $11.25 6 Ian 24MAR2008 MP $22.50 7 Chris 25MAR2008 CD $7.50 8 Anthony 25MAR2008 MP $16.25 9 Stephen 25MAR2008 CD $12.50 10 Erika 25MAR2008 MP $21.25
常用的格式有:
- 文本型:$HEXw.和$w.
- 日期型:DATEw.(输出为ddmmyy或者ddmmyyyy)、DATETIMEw.d(输出为ddmmyy:hh:mm:ss)、DAYw.(输出为dd)、EURDFDDw. 、JULIANw.、MMDDYYw.(输出为mmddyy或mmddyyyy)、TIMEw.d(输出为hh:mm:ss)、WEEKDATEw.(输出为工作日)、WORDDATEw.(输出为单词)。
- 数字型:BESTw.(自动选择)、COMMAw.d(逗号分隔)、DOLLARw.d(货币)、Ew.(科学计数法)、PDw.d、w.d(标准小数)
当然FORMAT还可以自定义factor型变量的输出格式,比如:
DATA carsurvey; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Cars.dat'; INPUT Age Sex Income Color $; PROC FORMAT; VALUE gender 1 = 'Male' 2 = 'Female'; VALUE agegroup 13 -< 20 = 'Teen' 20 -< 65 = 'Adult' 65 - HIGH = 'Senior'; VALUE $col 'W' = 'Moon White' 'B' = 'Sky Blue' 'Y' = 'Sunburst Yellow' 'G' = 'Rain Cloud Gray'; * Print data using user-defined and standard (DOLLAR8.) formats; PROC PRINT DATA = carsurvey; FORMAT Sex gender. Age agegroup. Color $col. Income DOLLAR8.; TITLE 'Survey Results Printed with User-Defined Formats'; RUN;
就可以把数字型的1,2转换为对应的文本male和female等,还可以把变量离散化,得到的输出为:
Survey Results Printed with User-Defined Formats 1 Obs Age Sex Income Color 1 Teen Male $14,000 Sunburst Yellow 2 Adult Male $65,000 Rain Cloud Gray 3 Senior Female $35,000 Sky Blue 4 Adult Male $44,000 Sunburst Yellow 5 Adult Female $83,000 Moon White
最终可以实现的自定义输出还包括简单的文本连接,比如:
* Write a report with FILE and PUT statements; DATA _NULL_; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Candy.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-11 Class @15 DateReturned MMDDYY10. CandyType $ Quantity; Profit = Quantity * 1.25; FILE 'c:\MyRawData\Student.txt' PRINT; TITLE; PUT @5 'Candy sales report for ' Name 'from classroom ' Class // @5 'Congratulations! You sold ' Quantity 'boxes of candy' / @5 'and earned ' Profit DOLLAR6.2 ' for our field trip.'; PUT _PAGE_; RUN;
可以给出若干连续的输出(注意DATA _NULL_;将不生成任何SAS的数据表):
Candy sales report for Adriana from classroom 21 Congratulations! You sold 7 boxes of candy and earned $8.75 for our field trip. ------------ Candy sales report for Nathan from classroom 14 Congratulations! You sold 19 boxes of candy and earned $23.75 for our field trip. ------------ Candy sales report for Matthew from classroom 14 Congratulations! You sold 14 boxes of candy and earned $17.50 for our field trip. ------------
SAS里面总结数据:MEANS
SAS当然还有类似于excel的数据透视表和R的data.table的模块,就是MEANS。可以输出的summary statistics包括最大值、最小值、平均值、中位数、余非缺失值个数、缺失值个数、范围、标准差、和等等。此外,还可以使用BY或者CLASS进行分组统计,VAR选择变量等。
比如:
DATA sales; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Flowers.dat'; INPUT CustomerID $ @9 SaleDate MMDDYY10. Petunia SnapDragon Marigold; Month = MONTH(SaleDate); PROC SORT DATA = sales; BY Month; * Calculate means by Month for flower sales; PROC MEANS DATA = sales; BY Month; VAR Petunia SnapDragon Marigold; TITLE 'Summary of Flower Sales by Month'; RUN;
可以实现:
Summary of Flower Sales by Month 1 --------------------------------- Month=5 --------------------------------- The MEANS Procedure Variable N Mean Std Dev Minimum Maximum --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Petunia 3 86.6666667 35.1188458 50.0000000 120.0000000 SnapDragon 3 113.3333333 41.6333200 80.0000000 160.0000000 Marigold 3 81.6666667 25.6580072 60.0000000 110.0000000 --------------------------------- Month=6 --------------------------------- Variable N Mean Std Dev Minimum Maximum --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Petunia 4 81.2500000 16.5201897 60.0000000 100.0000000 SnapDragon 4 97.5000000 47.8713554 60.0000000 160.0000000 Marigold 4 83.7500000 19.7378655 60.0000000 100.0000000 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
当然这些统计量也可以直接的写入一个SAS数据表,只需要加上一个OUTPUT就可以了。原数据:
756-01 05/04/2008 120 80 110 834-01 05/12/2008 90 160 60 901-02 05/18/2008 50 100 75 834-01 06/01/2008 80 60 100 756-01 06/11/2008 100 160 75 901-02 06/19/2008 60 60 60 756-01 06/25/2008 85 110 100
SAS代码:
DATA sales; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Flowers.dat'; INPUT CustomerID $ @9 SaleDate MMDDYY10. Petunia SnapDragon Marigold; PROC SORT DATA = sales; BY CustomerID; * Calculate means by CustomerID, output sum and mean to new data set; PROC MEANS NOPRINT DATA = sales; BY CustomerID; VAR Petunia SnapDragon Marigold; OUTPUT OUT = totals MEAN(Petunia SnapDragon Marigold) = MeanPetunia MeanSnapDragon MeanMarigold SUM(Petunia SnapDragon Marigold) = Petunia SnapDragon Marigold; PROC PRINT DATA = totals; TITLE 'Sum of Flower Data over Customer ID'; FORMAT MeanPetunia MeanSnapDragon MeanMarigold 3.; RUN;
最终结果为:
SAS PROC统计频率:FREQ
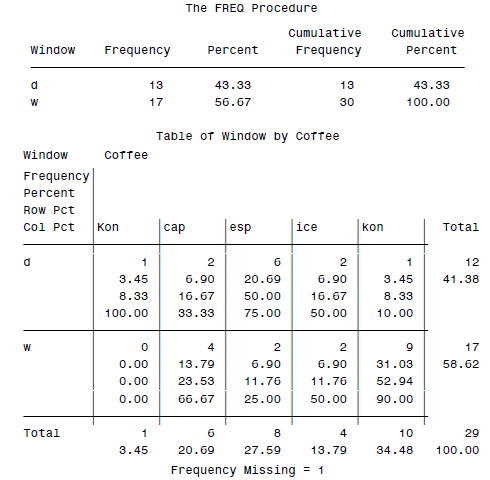
计数的话,就要靠SAS里面的FREQ模块了。比如我们有一个数据集:
esp w cap d cap w kon w ice w kon d esp d kon w ice d esp d cap w esp d cap d Kon d . d kon w esp d cap w ice w kon w kon w kon w ice d esp d kon w esp d esp w kon w cap w kon w
然后可以用FREQ来统计一些基本量:
DATA orders; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Coffee.dat'; INPUT Coffee $ Window $ @@; * Print tables for Window and Window by Coffee; PROC FREQ DATA = orders; TABLES Window Window * Coffee; RUN;
最终会得到一个2×5的表格:
SAS PROC汇报表格:TABULATE
基本看到TABULATE就可以想到那个著名的软件Tabular了...不过貌似SAS也自带了一个类似的表格模块。这个东西可以变得非常复杂,不过鉴于我一时半会儿还用不到,所以也没有细细看。抄个例子吧。
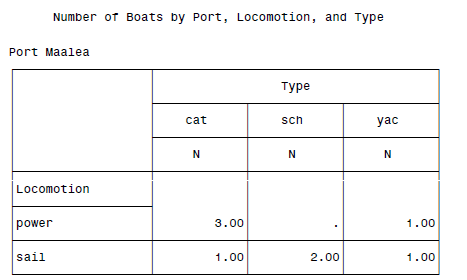
原数据:
Silent Lady Maalea sail sch 75.00 America II Maalea sail yac 32.95 Aloha Anai Lahaina sail cat 62.00 Ocean Spirit Maalea power cat 22.00 Anuenue Maalea sail sch 47.50 Hana Lei Maalea power cat 28.99 Leilani Maalea power yac 19.99 Kalakaua Maalea power cat 29.50 Reef Runner Lahaina power yac 29.95 Blue Dolphin Maalea sail cat 42.95
SAS代码:
DATA boats; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Boats.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-12 Port $ 14-20 Locomotion $ 22-26 Type $ 28-30 Price 32-36; RUN; * Tabulations with three dimensions; PROC TABULATE DATA = boats; CLASS Port Locomotion Type; TABLE Port, Locomotion, Type; TITLE 'Number of Boats by Port, Locomotion, and Type'; RUN;
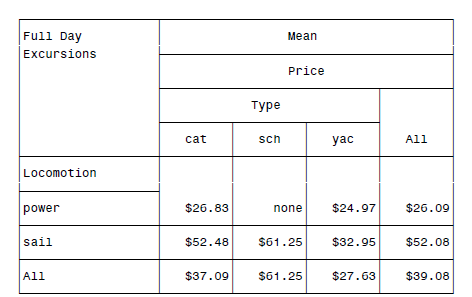
类似的,还可以增加统计量(类似于MEANS那里):
DATA boats; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Boats.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-12 Port $ 14-20 Locomotion $ 22-26 Type $ 28-30 Price 32-36; RUN; * PROC TABULATE report with options; PROC TABULATE DATA = boats FORMAT=DOLLAR9.2; CLASS Locomotion Type; VAR Price; TABLE Locomotion ALL, MEAN*Price*(Type ALL) /BOX='Full Day Excursions' MISSTEXT='none'; TITLE; RUN;
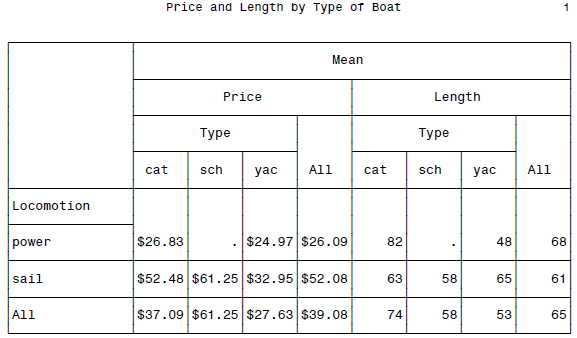
最后还可以混合FORMAT等等,可以变得相当的复杂。貌似这东西是美国劳工部鼓捣出来的格式...
DATA boats; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Boats.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-12 Port $ 14-20 Locomotion $ 22-26 Type $ 28-30 Price 32-36 Length 38-40; RUN; * Using the FORMAT= option in the TABLE statement; PROC TABULATE DATA = boats; CLASS Locomotion Type; VAR Price Length; TABLE Locomotion ALL, MEAN * (Price*FORMAT=DOLLAR6.2 Length*FORMAT=6.0) * (Type ALL); TITLE 'Price and Length by Type of Boat'; RUN;
BOSS级汇报表格呈现了...
我只能感慨,不愧是商业软件啊,用户需求考虑的真的是特别的周到...这种费时费力做汇报表格的事情也被搞定了,强悍。
SAS里面的报告:REPORT
还有一个REPORT,看到有TABULATE的时候我已经不奇怪并略略的有些期待一个做报告的模块出现了。这东西基本就是前面几个的超级混合体,反正你想搞到的汇报模式总是能够搞出来的。
又是一堆数据:
17 sci 9 bio 28 fic 50 mys 13 fic 32 fic 67 fic 81 non 38 non 53 non 16 sci 15 bio 61 fic 52 ref 22 mys 76 bio 37 fic 86 fic 49 mys 78 non 45 sci 64 bio 8 fic 11 non 41 fic 46 ref 69 fic 34 fic 26 mys 23 sci 74 ref 15 sci 27 fic 23 mys 63 fic 78 non 40 bio 12 fic 29 fic 54 mys 67 fic 60 fic 38 sci 42 fic 80 fic
然后一堆SAS代码:
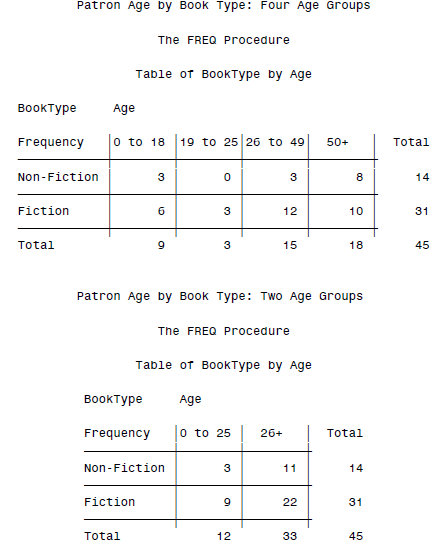
DATA books; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\LibraryBooks.dat'; INPUT Age BookType $ @@; RUN; *Define formats to group the data; PROC FORMAT; VALUE agegpa 0-18 = '0 to 18' 19-25 = '19 to 25' 26-49 = '26 to 49' 50-HIGH = ' 50+ '; VALUE agegpb 0-25 = '0 to 25' 26-HIGH = ' 26+ '; VALUE $typ 'bio','non','ref' = 'Non-Fiction' 'fic','mys','sci' = 'Fiction'; RUN; *Create two way table with Age grouped into four categories; PROC FREQ DATA = books; TITLE 'Patron Age by Book Type: Four Age Groups'; TABLES BookType * Age / NOPERCENT NOROW NOCOL; FORMAT Age agegpa. BookType $typ.; RUN; *Create two way table with Age grouped into two categories; PROC FREQ DATA = books; TITLE 'Patron Age by Book Type: Two Age Groups'; TABLES BookType * Age / NOPERCENT NOROW NOCOL; FORMAT Age agegpb. BookType $typ.; RUN;
当然,简单的计算和分类统计也不在话下:
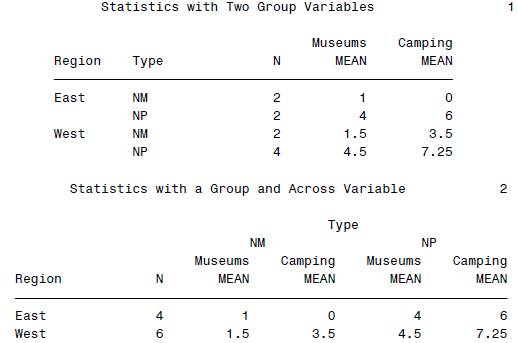
DATA natparks; INFILE 'c:\MyRawData\Parks.dat'; INPUT Name $ 1-21 Type $ Region $ Museums Camping; RUN; *Statistics in COLUMN statement with two group variables; PROC REPORT DATA = natparks NOWINDOWS HEADLINE; COLUMN Region Type N (Museums Camping),MEAN; DEFINE Region / GROUP; DEFINE Type / GROUP; TITLE 'Statistics with Two Group Variables'; RUN; *Statistics in COLUMN statement with group and across variables; PROC REPORT DATA = natparks NOWINDOWS HEADLINE; COLUMN Region N Type,(Museums Camping),MEAN; DEFINE Region / GROUP; DEFINE Type / ACROSS; TITLE 'Statistics with a Group and Across Variable'; RUN;
SAS数据总结综述
我的感觉是,MEANS, TABULATE和REPORT这三个模块各有千秋,基本就是可以替代EXCEL的数据透视表,虽然效率上说不好谁比谁高...随便哪一个用习惯了就好,反正又不是天天出政府报告的,我就懒得深究了。